Introduction
If you’re a proud owner of a Russian tortoise, you know that these charming reptiles can sometimes be picky eaters. It’s vital to be aware of the signs indicating that your tortoise may not be eating properly. Common symptoms include lethargy and refusal to eat, which could stem from a range of issues. Young tortoises, in particular, may require special attention as their nutritional needs differ from those of adult tortoises. Factors like environmental conditions and improper diets can affect their appetite. Understanding these elements will help you connect about your tortoise’s health and ensure it gets the support it needs.
Regular monitoring of your tortoise’s behavior is essential. If your baby tortoise isn’t eating for more than three days, it might be time to consult an accredited veterinarian. Common medical conditions can unintentionally lead to loss of appetite, making it crucial to take prompt action. Providing insight and home care based on expert answers can make a significant difference in your pet’s well-being and overall health.
Key Takeaways
- Regularly monitor your Russian tortoise’s behavior for signs of not eating, such as lethargy or refusal to eat.
- Creating a spacious and comfortable tortoise enclosure with appropriate basking areas is essential for encouraging appetite.
- Ensure your tortoise has constant access to fresh water to maintain hydration and support digestion.
- Calcium is vital for your tortoise’s health; without it, they may exhibit symptoms like swollen eyes or lethargy.
- A diverse diet, including calcium-rich foods, is crucial for maintaining your tortoise’s health and preventing loss of appetite.
- If your tortoise hasn’t eaten for more than three days, it’s important to consult a veterinarian to rule out underlying health issues.
Identifying Signs Your Russian Tortoise is Not Eating
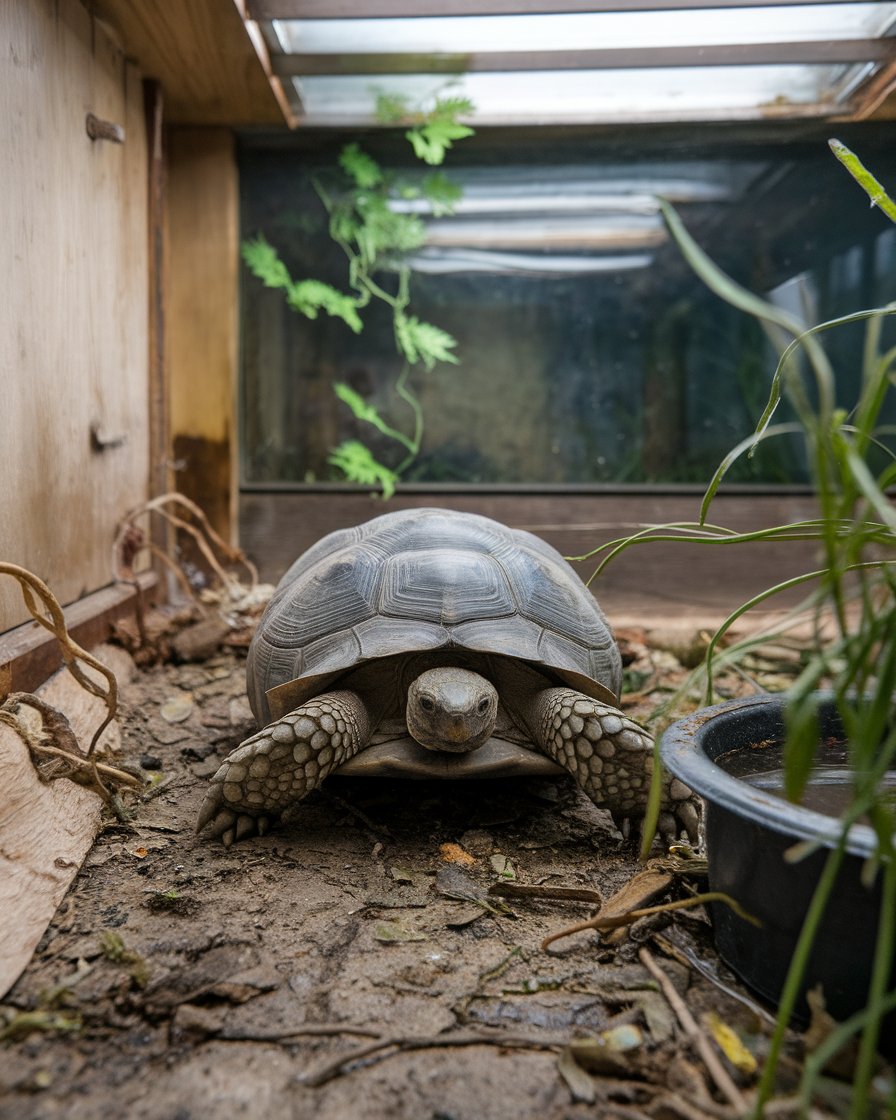
If you notice your Russian tortoise isn’t eating, it’s essential to identify the signs early. A tortoise may show indicators like lethargy, swollen eyes, or an overall lack of movement. It’s common for species of tortoise to experience a loss of appetite, especially during temperature fluctuations. You should ensure that the enclosure is deep enough for your tortoise to feel secure. A warm basking area with proper UVB light can encourage your tortoise to eat. If your pet has stopped eating for more than three days or refuses to eat its usual diet, this may indicate underlying health issues. Monitoring your tortoise’s behavior and diet can help you connect about your tortoise’s health needs more effectively. If your tortoise is likely not eating, providing support of your ill tortoise is crucial.
Common Reasons Why Your Russian Tortoise Might Not Be Eating
Temperature Issues
Russian tortoises need a warm environment to digest food properly. If the temperature drops below 65°F, they may stop eating as their metabolism slows down.Dietary Preferences
Tortoises can be picky eaters. If they dislike the food offered, they may refuse to eat. Ensure you provide fresh, varied options like dark leafy greens and occasional fruits to stimulate their appetite.Stress and Anxiety
Changes in their environment or routine can stress your tortoise, leading to a temporary loss of appetite. Creating a quiet, secure space can help them feel more comfortable.Constipation
If your tortoise is constipated, it may also stop eating. Regular hydration and a diet rich in fiber can help prevent this issue.Medical Conditions
Serious health issues, such as respiratory infections or parasites, can cause a tortoise to lose its appetite. If you notice other symptoms, consult a veterinarian.Hibernation Behavior
During colder months, tortoises may enter a state of brumation, leading to decreased eating. Monitor their overall health during this time and consult a vet if you have concerns.
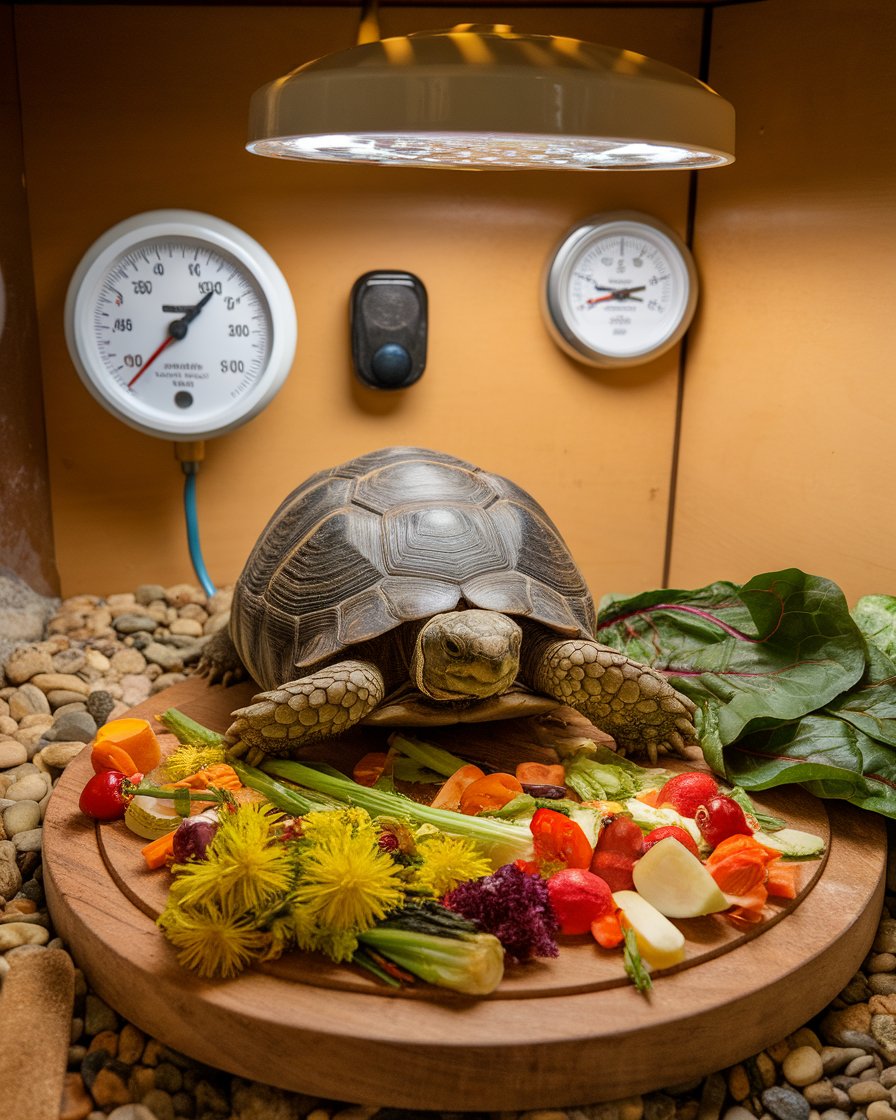
How to Create a Comfortable Tortoise Enclosure
Creating a comfortable tortoise enclosure is crucial for your pet’s well-being and appetite. The enclosure should be spacious, allowing your Russian tortoise to move around freely and explore. Make sure to provide a basking area with radiant heat without light, where your tortoise can warm up. The substrate should be deep enough to facilitate digging, as this behavior is natural for tortoises. Incorporating hiding spots and climbing structures can also help reduce stress. Regularly monitor the enclosure’s humidity levels to ensure a suitable environment. A comfortable and enriching space encourages your tortoise to eat and thrive, preventing issues associated with a lack of activity.
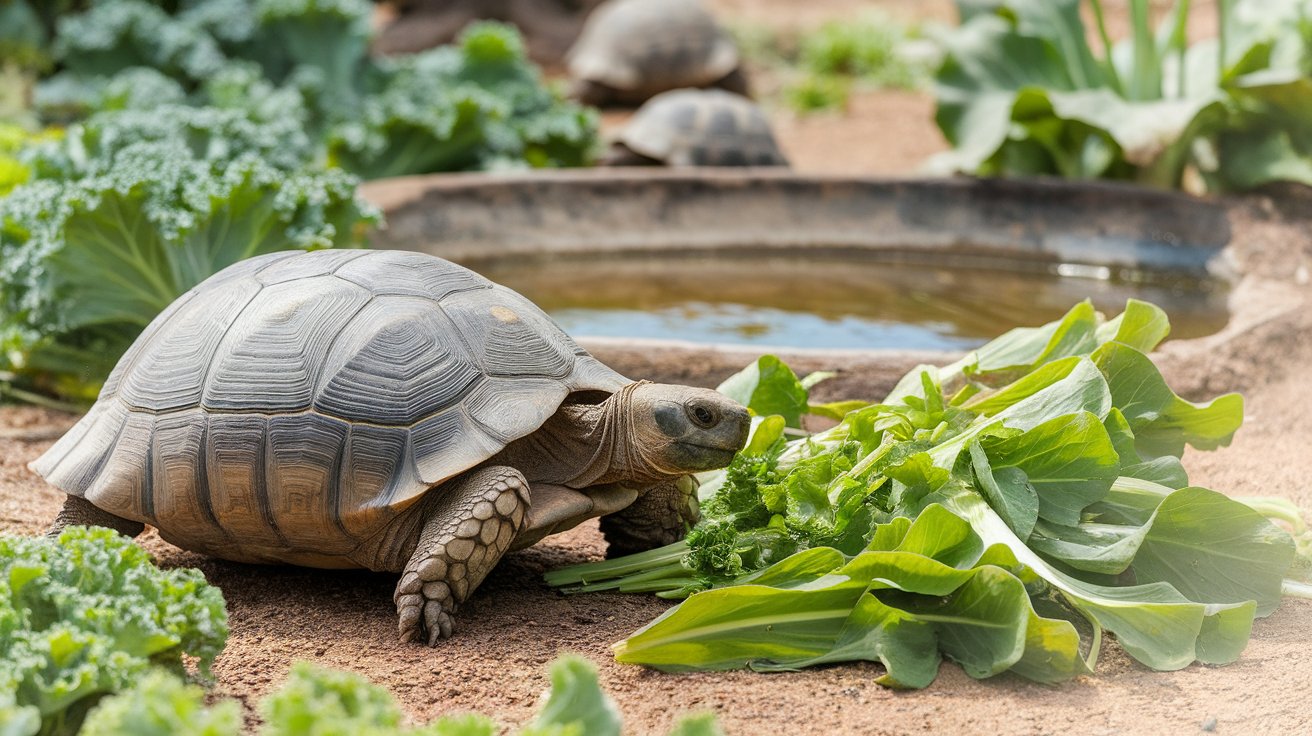
The Role of Hydration in Your Tortoise’s Diet
Hydration plays a vital role in maintaining your tortoise’s overall health. Tortoises need access to fresh water at all times; a shallow pan of water can encourage them to drink more frequently. Proper hydration aids digestion and helps maintain the necessary calcium and vitamin levels in their body. If your tortoise is dehydrated, it may stop eating, leading to further health complications. Providing warm water baths can also help hydrate your tortoise and stimulate its appetite. Monitoring your tortoise’s water intake and ensuring it stays hydrated can significantly influence its willingness to eat and overall health.
Understanding the Importance of Calcium for Your Tortoise’s Health
Calcium is vital for the overall health of your Russian tortoise. It plays a critical role in bone development and helps prevent metabolic bone disease. Tortoises require a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D3, which can be obtained from natural sources like dandelions and leafy greens. Without proper calcium intake, your tortoise may exhibit signs of illness, such as a swollen jaw or difficulty moving. Additionally, make sure your tortoise has access to fresh water and that the enclosure maintains appropriate humidity levels. A well-balanced diet, including calcium supplements, is also a good idea to ensure that your tortoise is thriving and maintains a healthy appetite.
Case Study: The Impact of Calcium Deficiency in Russian Tortoises
Calcium deficiency is a common issue that can significantly affect the health of Russian tortoises, leading to serious conditions like Metabolic Bone Disease (MBD). One notable case involved a juvenile tortoise that exhibited lethargy, swollen limbs, and a softened shell. Upon examination, it was found that the tortoise was not receiving adequate calcium or vitamin D3, essential nutrients for bone development and overall health.
The veterinarian recommended a dietary adjustment, including calcium-rich foods such as dark leafy greens and a calcium supplement. Additionally, the tortoise was provided access to UVB light, which is crucial for calcium absorption. Over the following months, the tortoise’s condition improved markedly, demonstrating increased energy levels and a return to normal activity.
Signs That Your Tortoise May Need Additional Calcium
Calcium deficiency can lead to serious health issues in your tortoise. If your pet displays signs like swollen eyes or lethargy, it may be time to increase its calcium intake. Regularly offering calcium-rich foods, such as dark leafy greens and commercial calcium supplements, can support your tortoise’s health. It’s also essential to provide vitamin D3, as this helps the body absorb calcium effectively. If your tortoise is not eating or seems less active, consider consulting a vet to evaluate its calcium levels. By ensuring your tortoise receives enough calcium, you can promote strong bones and overall well-being.
Adjusting Diet for Optimal Health in Your Tortoise
To maintain optimal health in your Russian tortoise, adjusting its diet is essential. Tortoises may not eat if their diet lacks variety or includes foods they dislike. Offer a range of fresh vegetables, fruits, and commercial tortoise pellets to entice your pet to eat. Additionally, include calcium and vitamin-rich options to support healthy growth and digestion. Monitor your tortoise’s reaction to new foods, as some may refuse certain items. It’s a good idea to offer food twice a day to encourage regular eating habits. By diversifying your tortoise’s diet, you can help ensure it receives all necessary nutrients for a healthy life.
Common Causes of Loss of Appetite in Tortoises
A tortoise may not be eating for several reasons, and understanding these can help you provide better care. Common causes include environmental stress, such as changes in temperature or humidity levels in the enclosure. Additionally, a sick tortoise might stop eating, indicating underlying health issues like respiratory infections or improper diet. It’s essential to observe your tortoise closely; if it appears otherwise acting normal but won’t eat, consider factors like food freshness and variety. Connecting with a local veterinarian who specializes in reptile medicine can give you more insight into what may be causing these signs and how to support your tortoise effectively.
Recognizing Environmental Stressors for Your Tortoise
Environmental stressors can significantly impact your tortoise’s eating habits. Factors such as temperature fluctuations, inadequate lighting, or high humidity levels may cause a tortoise to stop eating. Ensure your enclosure mimics the natural habitat of your tortoise species, providing appropriate basking spots and hiding areas. Monitoring the temperature in the cool and warm areas of the enclosure is crucial to maintain a healthy environment. If you notice your tortoise is lethargic or refusing to eat, consider if recent changes in the environment could be affecting its behavior. Identifying and addressing these stressors is key to encouraging your tortoise to eat.
Common Medical Conditions That Affect Tortoise Eating Habits
Several common medical conditions can lead to a tortoise not eating. Respiratory infections, for instance, may cause lethargy and a loss of appetite. Other health issues, like gastrointestinal problems or parasites, can also impact eating habits. If your tortoise has not eaten for an extended period or shows signs of illness, consulting a veterinarian is essential. Regular check-ups with a vet experienced in reptile medicine can help catch these conditions early. Understanding the potential medical issues affecting your tortoise allows you to respond promptly and seek the necessary treatment to restore its appetite.
“The affection towards all living beings is the most honorable characteristic of humanity.” – Charles Darwin
When to Consult a Vet for Your Tortoise’s Eating Issues
If your tortoise hasn’t eaten for more than three days, it’s crucial to consult a vet. Loss of appetite can signal serious health issues that warrant veterinary evaluation. A licensed and accredited veterinarian can provide insight into your tortoise’s condition and suggest home care options. If your tortoise shows signs like swollen eyes or lethargy, these may be red flags indicating it needs immediate attention. Keeping a photo or video of your tortoise might be helpful for the vet to assess the situation more accurately. Early intervention is key, so don’t hesitate to seek professional advice to ensure your tortoise remains healthy and vibrant.
Veterinary Solutions for a Tortoise That Won’t Eat
If your tortoise refuses to eat, a visit to the veterinarian is crucial. A licensed veterinarian can conduct a thorough examination and provide insight into potential health issues affecting your tortoise. They may suggest dietary adjustments or recommend specific medications if your tortoise is sick. In some cases, you might need to force feed an uncooperative tortoise to ensure it receives essential nutrients. Discussing your tortoise’s symptoms and behavior with the vet can help them offer tailored solutions and advice based on the information provided. Prompt veterinary care is vital to ensure your tortoise’s health and well-being.
Tips for Encouraging Your Tortoise to Eat Again
Encouraging your tortoise to eat again may require patience and creativity. Start by offering fresh, appealing foods like dandelions or other greens that your tortoise enjoys. You can also try varying the presentation of food, such as chopping it into smaller pieces or placing it in different locations in the enclosure. Providing a warm water bath can stimulate appetite and hydration. If your tortoise is still not eating after trying these methods, it might be time to consult a veterinarian for further evaluation. Regularly monitoring your tortoise’s behavior and appetite will help ensure it remains healthy and engaged with its food.
Conclusion
In summary, ensuring your Russian tortoise remains healthy and happy requires vigilance and proper care. It’s essential to regularly monitor your tortoise for signs of illness, such as lethargy or a refusal to eat. Factors like environmental conditions, hydration, and a balanced diet rich in calcium can significantly affect their appetite. If you notice that your baby tortoise is not eating for more than three days, it’s vital to consult an accredited veterinarian who specializes in reptiles.
By providing adequate support for your ill tortoise, you can address potential issues early on. Remember, a comfortable enclosure and a varied diet not only encourage your tortoise to eat but also promote overall well-being. With proper attention, your tortoise can thrive and continue to be a cherished part of your family for years to come. Always stay informed and connected about your tortoise’s needs to ensure a healthy and fulfilling life.